CTI is expected to provide adequately trained Consultants to coordinate with the application Verification and
Validation as a separate part of the project from development. This part is driven by its own quality and user
goals that are different from development.
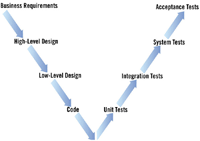
The level of Test is the primary focus of a system and derives from the way a software system is designed and
built up. The V Model maps the types of Test to each stage of development
Verification and Validation Planning:
V&V Plan and Effort Estimations :
Just like the project Development Plan and Quality Plan, Verification and
Validation planning should be generated early, initially as part of the Development Plan, and later as a standalone
document. During the development activities, system requirements & architecture will likely change and impact the
test strategy, or conversely the V&V strategy for regulatory compliance may change which in turn can impact system
requirements and architecture tradeoffs.
Regulatory Compliance Strategies
This activity requires both research and expert knowledge. It typically includes
UL testing, EMI/EMC testing, CE Mark strategy, and compliance with established development SOPs and guidelines for ISO.
For wireless RF products and for many medical devices involving disposables, special certifications and biocompatibility
testing are needed.
Development of Test Objectives
Test objectives should be developed early to help remove ambiguity from the system
requirements. A common fate of a project is to release too early, or become mired at the other extreme, stuck in testing
because there are no clear objects established to determine completion criteria. The project Development Plan should state
whether testing is a debugging exercise or does the business use testing to access project and release risks. In addition
to strictly functional testing, the project V&V team needs to consider usage goals for the project: performance,
reliability, or usability.
Use of Simulation Environments
Simulations assist in both development and verification activities. During
development, simulation can be used to take the place of physical components that are not yet available.
The same is true for verification activities in that Test Objectives and procedures may be evaluated before
the product is available using simulated components. Simulation can also be used to control or establish a
known test environment for regression testing purposes and automated testing. Early and informed selection of
simulation environments can result in reuse of these in product development, debugging, testing, clinical trials,
and manufacturing.
Software Maintenance and Upgrades
Modifications to existing products these are typically underestimated
because they tend to appear smaller and more limited than a full development activity. However, all of the processes
followed for the initial development project need to be executed in some form for maintenance and upgrades.
Independent Verification and Validation can be carried out with
-
Automated testing
-
Electromagnetic Compatibility·
-
Electrostatic Discharge
-
Fault-based testing
-
Functional testing
-
Future date testing
-
Hybrid testing
-
Incremental analysis
-
Initial Operational Test and Evaluation
-
Integration testing
-
Interface analysis
-
Intrusive Testing
-
Manual testing
|